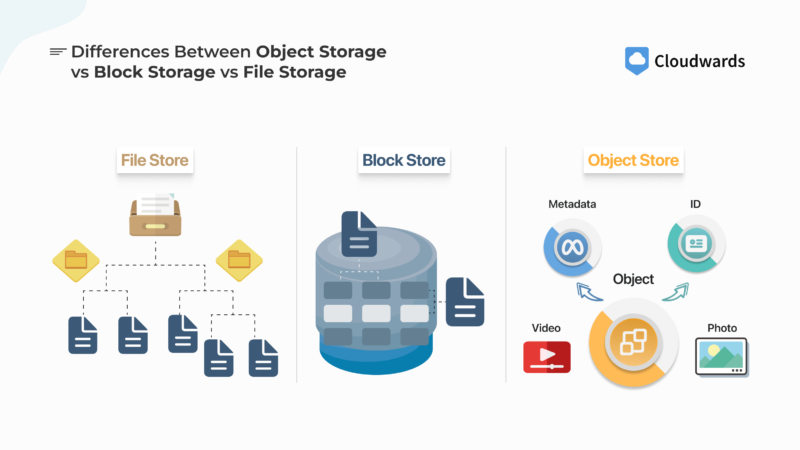
In this comparative analysis, we look at object storage vs file storage vs block storage, the three main organizational patterns for storing cloud data. Each one offers a unique type of storage structure and accessibility, which affects their use cases, especially as it relates to cloud computing.
The biggest difference between these storage systems is that object storage is unstructured (has no data organization model) and relies on metadata for identification and management, while file storage and block storage have more structure to their storage patterns. Keep reading to learn more about object, block and file storage.
Differences Between Object Storage vs Block Storage vs File Storage
Block storage is more efficient than object and file storage,
but object storage is the most scalable.
Below is a summary of the key differences between object storage, block storage and file storage:
| Feature: | Object-Based Storage | Block-Based Storage | File-Based Storage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Storage Architecture | Stores data as objects with metadata in a flat namespace | Divides data into equal-sized blocks and stores them with minimal metadata | Stores data as files in a hierarchical structure for intuitive access |
| Storage Capacity | Typically unlimited | Capacity determined by provider, but usually up to terabytes | Maximum capacity varies by provider but usually up to terabytes |
| Performance | Ideal for storing large data and media files | High throughput, high efficiency and low latency | Optimized for organized, shared data access |
| Metadata Management | Unlimited and customizable metadata | Limited metadata for efficient transfer | Various file-related metadata, such as file type, modification dates and size |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Limited scalability | Limited scalability |
| Cost | Cost-effective for large volumes of data | Typically more expensive than object storage | Can get expensive with increasing storage size |
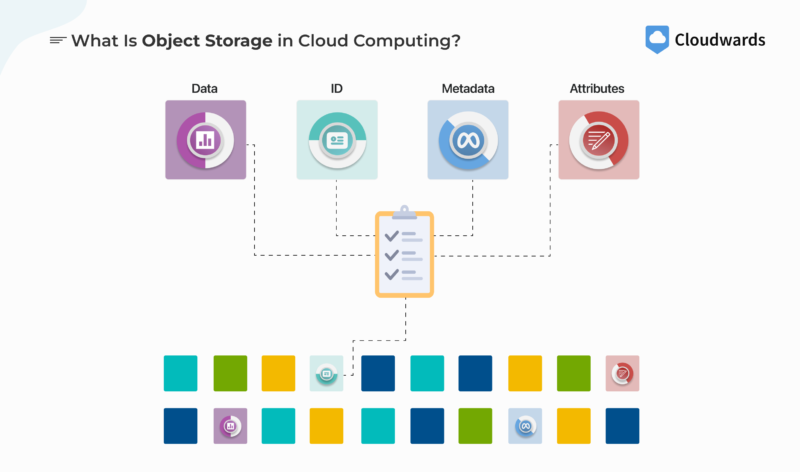
What Is Object Storage in Cloud Computing?
Object storage hashes object IDs to ensure objects with
the same content have the same ID.
Object storage in cloud computing stores unstructured data in its original format as an object, which consists of the data and its metadata. It stores these objects in containers called buckets, which can scale in size.

- Demystify cloud storage terminology and key concepts in plain language
- Discover easy-to-implement techniques to securely backup and sync your data across devices
- Learn money-saving strategies to optimize your cloud storage costs and usage
Object storage uses a flat namespace, so all the objects in a bucket exist at the same level. However, for easy access, handling and identification, data are stored with their metadata, ID and attributes.
Cloud object storage systems are ideal when trying to store large volumes of data — such as for media or big data analytics — at relatively low prices. You can use them for large files, unstructured data, backups, archives and more.
Blob Storage vs Object Storage
Blob storage is a type of object storage. “Blob” stands for “binary large object” and refers to large chunks of binary data — data that is not text – such as audio files, images and video files.
Whereas object storage stores data, including blobs, in its original upload format along with metadata, blob storage is a type of object storage that stores binary large objects. In other words, blob storage is object storage, but not all object storage is blob storage.
What Is Block Storage in Cloud Computing?
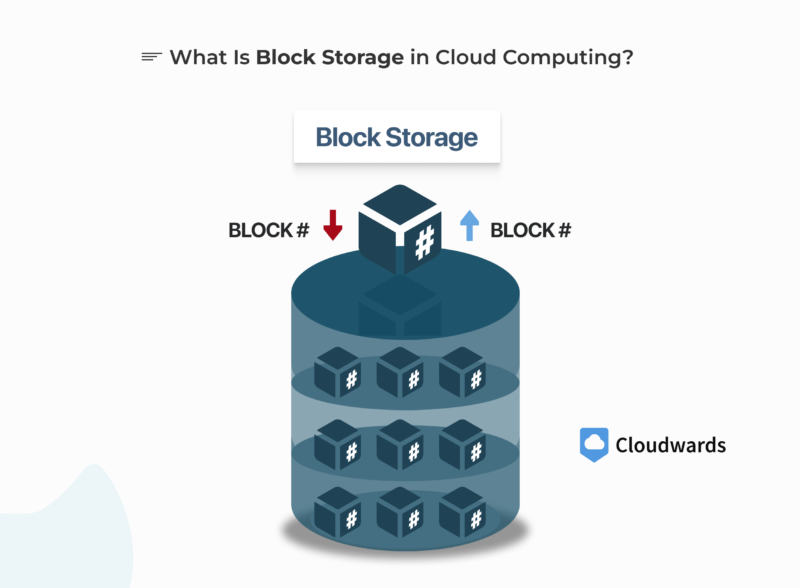
Blocks in block storage can be accessed individually, enhancing efficiency.
Block storage in cloud computing splits and stores data into equal-sized blocks. Each block gets limited metadata, which typically includes only the block’s unique identifier — the piece of data needed to access the block.
The upside of block storage having limited metadata is enhanced data transfer efficiency and speed. That aside, block storage allows direct access to each data block, so you don’t necessarily have to access all of the data when performing read-and-write operations. In other words, you can access only part of the data, which ensures fast operations.
Block storage systems are raw storage forms that are ideal for low-latency input/output (I/O) operations. They are used for real-time analytics, operating system installations and general high-performance computing.
What Is File Storage in Cloud Computing?
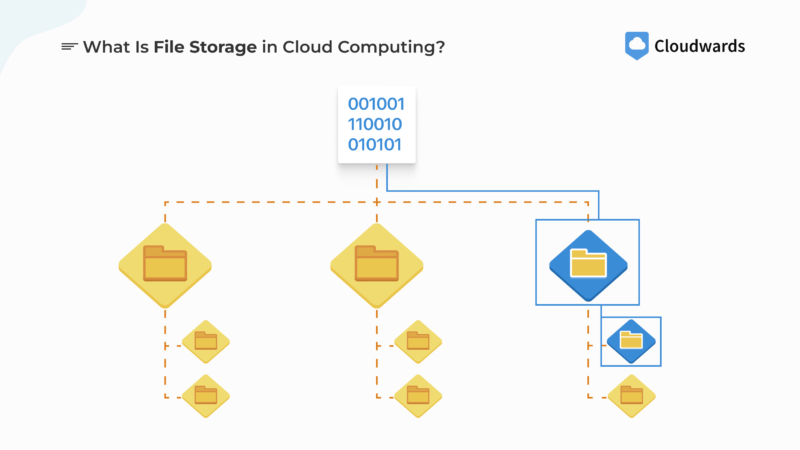
File storage design has a flow that is easy for people to navigate.
File storage in cloud computing stores data as files in a hierarchical namespace called a filesystem. It follows pretty much the same pattern as a physical filing system where files are placed in folders, the folders are stored on shelves and the shelves are housed in a room.
File storage systems store files with metadata such as file type, size and modification date, but compared to object storage, the metadata is limited. File storage is designed for shared file access, as its structure follows a pattern that allows for instinctive human access. You can readily go down the hierarchical path of a filesystem to locate files.
Use Cases for Block Storage vs Object Storage vs File Storage
Understanding the use cases for block storage, object storage and file storage is crucial for optimal data management. Let’s explore these use cases below:
Pros & Cons of Block vs File vs Object Storage
Final Thoughts
Object storage is your best bet when you want to store data in large volumes without burning through your wallet. However, you should choose file storage when you need shared data access and block storage when you need efficient and fast I/O operations.
In your opinion, which of these three storage types suits the most use cases? Which of them do you have the most experience with? Share your opinion about cloud storage with us below, and once again, thanks for reading.
FAQ: Objects, Blocks and Files
-
The difference between block, file and object storage is that block storage splits data and stores it in equal-sized blocks, file storage organizes and stores data in a hierarchical filesystem, and object storage stores data in its original form in an expandable storage unit.
-
Block storage stores data divided into blocks of equal size, while blob storage (another type of object storage) stores data — like image, video or audio files — in its original format along with its metadata in a flat namespace.
-
Amazon S3 is an object storage service; it stores data as objects in containers called buckets.
Sources