Choosing between LabVIEW vs MATLAB can be challenging. Each graphical programming language has unique data analysis, engineering, and automation strengths. We’ll explain the main differences and guide you to the best choice for your needs.
What is LabVIEW?

LabVIEW is a graphical programming environment designed to make it easier to develop test systems. It offers intuitive programming tools, seamless connectivity with various instruments, and integrated user interfaces. It allows users to quickly build automated test systems and supports integration with other popular languages like Python, C, and .NET.
What is MATLAB?
MATLAB is a programming and numeric computing platform used by engineers and scientists for data analysis, algorithm development, and modeling. It combines an intuitive desktop environment for iterative analysis and design with a language directly supporting matrix and array mathematics. MATLAB also offers powerful visualization tools, extensive toolboxes for specialized tasks, and the capability to scale computations to clusters, GPUs, and cloud environments.
LabVIEW vs MATLAB Features
Both LabVIEW and MATLAB. Here’s a breakdown of their key features to help you compare:
LabVIEW Features
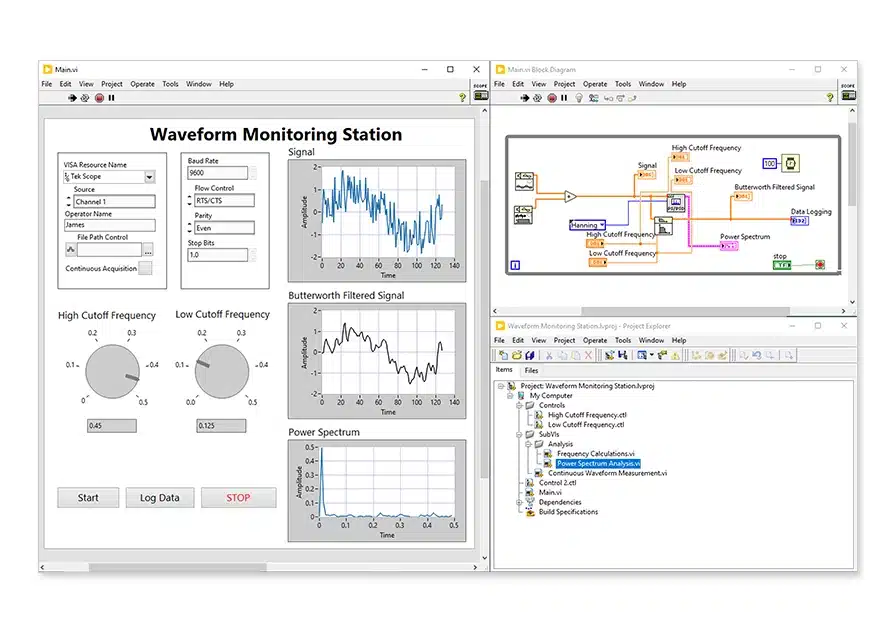
- Intuitive Programming: LabVIEW offers a visual interface for building test systems. The graphical programming design accelerates development by removing complex coding requirements.
- Cross-Platform Connectivity: LabVIEW can connect with instruments from any vendor. This compatibility broadens its utility across various industries and test environments.
- Analysis Functions Library: It includes thousands of built-in analysis tools. These tools help engineers gain insights from data without needing external software.
- Integrated User Interface: LabVIEW has an integrated user interface for monitoring and controlling tests. This enables real-time visualization and quick adjustments during tests.
- LabVIEW+ Suite: The LabVIEW+ Suite bundles additional software for measurement, analytics, and test execution. It supports engineers needing more than basic testing capabilities.
- Training and Support: LabVIEW provides training options, including on-demand courses. Engineers can improve their skills with advanced courses for specific application needs.
MATLAB Features
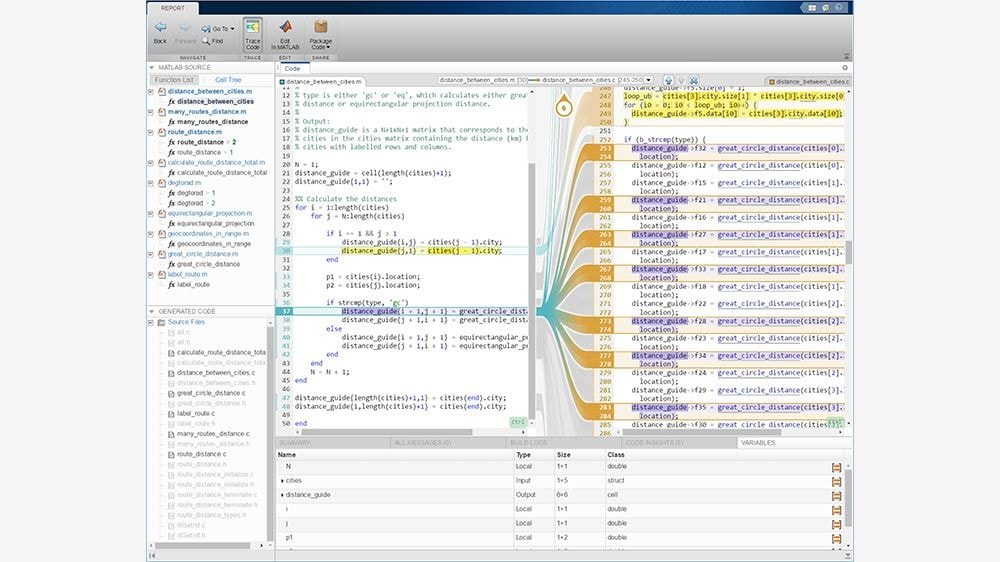
- Iterative Analysis and Design: MATLAB’s desktop environment supports an iterative approach to analysis. This structure lets users refine algorithms in real time for faster insights.
- Matrix-Based Programming: MATLAB’s language is optimized for matrix and array operations. This makes it especially useful for data manipulation and mathematical computation.
- Live Editor: Create scripts with code, output, and formatted text in one place. The Live Editor provides a workspace that combines documentation and computation seamlessly.
- Scalability Across Systems: MATLAB can scale to clusters, GPUs, and cloud services. This scaling feature allows users to handle large datasets without rewriting code.
- Toolbox Variety: MATLAB includes rigorously tested, professional-grade toolboxes. These toolboxes span fields like control systems, signal processing, and machine learning.
- Cloud and Hardware Integration: MATLAB connects to cloud environments (AWS, Azure) and integrates with hardware. It also enables deployment to embedded systems, allowing direct execution on processors and FPGAs.
- Industry Applications: MATLAB supports control systems, deep learning, predictive maintenance, and more. It’s widely used in industries requiring data analysis, simulation, and algorithm deployment.
LabVIEW vs MATLAB Pricing
LabVIEW Pricing

Standard License
- Annual: $900
- Designed for commercial, government, or organizational use. Includes MathWorks Software Maintenance Service for updates and support during the subscription term. Pricing excludes applicable taxes.
Startups License
- Annual: $3650
- For approved early-stage companies. This license includes MATLAB, Simulink, and over 90 add-on products. Contact MathWorks for specific pricing and options.
Academic License
- Annual: $262
- Made for faculty and researchers in educational institutions. Provides access to MATLAB and Simulink for academic purposes. Pricing varies by institution type and region.
Student License
- One-time Fee: $69
- An affordable, one-time option for students engaged in academic coursework. Includes MATLAB, Simulink, and 10 add-ons, with limitations for non-commercial, personal use.
Home License
- One-time Fee: $119
- For individual, non-commercial use. Offers MATLAB software for personal projects and hobbyist applications, excluding any organizational, governmental, or academic use.
MATLAB Pricing

LabVIEW Base
- Starting at: $528/year
- Ideal for creating simple test and measurement applications. Includes tools to acquire data from hardware, communicate with industry protocols, create interactive UIs, and perform basic data analysis.
LabVIEW Full
- Starting at: $1,664/year
- Suitable for applications requiring advanced analysis or signal processing. Includes all Base capabilities plus algorithms for curve fitting, differential equations, linear algebra, and signal processing for measurement and control. I
LabVIEW Professional
- Starting at: $2,750/year
- Designed for engineers needing software engineering tools for deployment and reporting. Includes Full capabilities, plus Application Builder for creating standalone applications, graphical code comparison, Microsoft Office report generation, and database connectivity for managing data in local and remote databases.
LabVIEW+ Suite
- Starting at: $3,995/year
- Solid suite for engineers developing modular, high-level test systems with faster time to market. Includes all Professional features, NI TestStand for test sequencing, NI InstrumentStudio for PXI measurements, NI FlexLogger for scalable data logging, and NI DIAdem for data visualization and reporting.
What are the main differences between MATLAB and LabVIEW?

Purpose:
- MATLAB: Ideal for numerical computing, data analysis, and algorithm development.
- LabVIEW: Best for test system development, data acquisition, and real-time monitoring.
Programming Style:
- MATLAB: Text-based, optimized for matrix and mathematical operations.
- LabVIEW: Graphical, using a visual interface for faster prototyping and testing.
Applications:
- MATLAB: Used in fields requiring complex computations (e.g., data analysis, control systems).
- LabVIEW: Common in industries like R&D, automotive, and manufacturing for live data handling.
Which software is better for data analysis and visualization?
MATLAB is generally better for data analysis and visualization. It provides extensive visualization tools, specialized toolboxes for fields like machine learning and signal processing, and features like the Live Editor, which combines code, output, and formatted text. MATLAB’s matrix-based language makes it efficient for data manipulation and computational tasks.
LabVIEW offers basic visualization tools suited for real-time data monitoring, but it’s more focused on data acquisition and control systems rather than in-depth data analysis.
In summary:
- Choose MATLAB for powerful data analysis, simulations, and algorithm-intensive applications.
- Choose LabVIEW for streamlined test system development, real-time data acquisition, and user interface design.
Do people still use LabVIEW?
Yes, LabVIEW is still widely used in various industries, particularly in areas that require quick prototyping, data acquisition, and control systems. It’s especially popular in:
- Research and Development
- Aerospace and Defense
- Automotive
- Manufacturing
Final thoughts

You should choose between LabVIEW and MATLAB based on your project needs. MATLAB is great for data analysis, simulation, and algorithm development. LabVIEW is ideal for test systems, data acquisition, and real-time monitoring. Each platform has unique advantages, so choose the best one for your needs.
MATLAB is often the preferred choice for engineers focused on complex computations. It supports numerical analysis, data manipulation, and visualization. LabVIEW is better for creating automated test systems. With LabVIEW, engineers can streamline data acquisition and control tasks efficiently.




