The technology giant IBM has secured a 4D printing patent from the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) for a breakthrough method that transports particles using innovative materials.
According to the patent details, these innovative materials leverage shape memory alloys or polymers that react to external stimuli such as temperature, light, magnetism, or electric current.
Once deformed, these materials can revert to their original shape, allowing researchers to induce movement and transport micron-sized particles—a task often challenging with conventional methods.
How IBM’s 4D Printing Technology Works
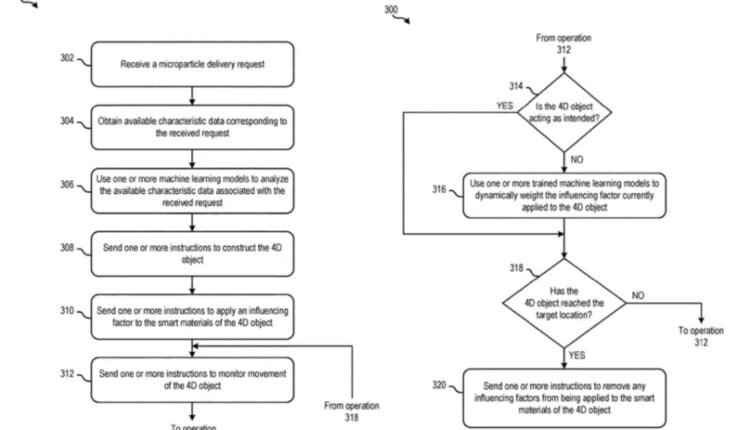
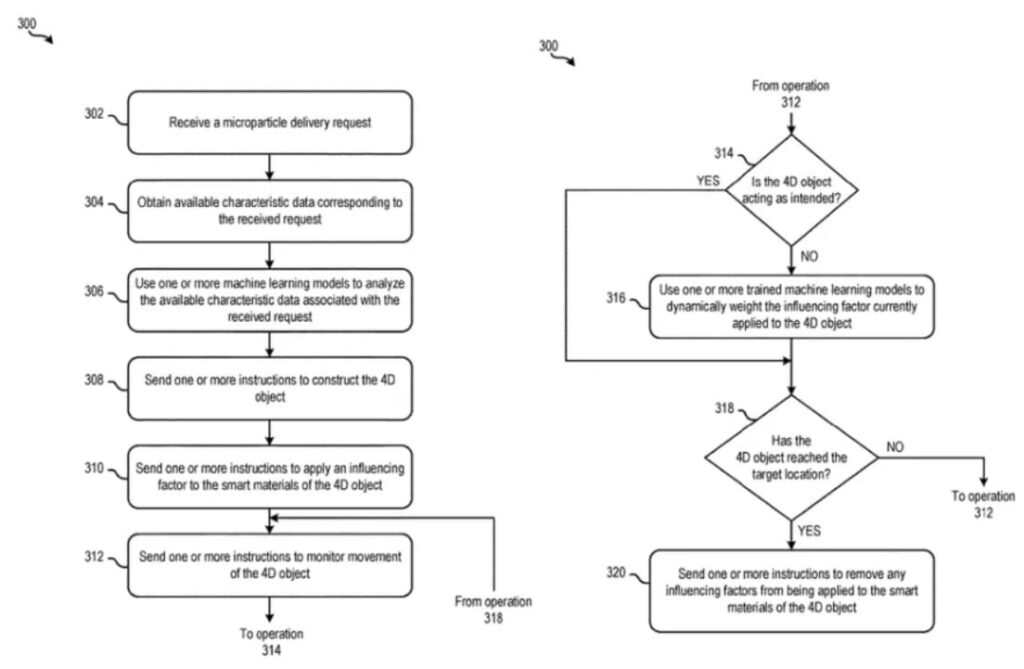
To utilize this 4D material transport, users must:
- Set up the delivery route and its environmental conditions
- Document the size, shape, weight, and composition of the item
- Apply machine learning algorithms to determine the correct stimulus
Depending on the conditions, heat, light, or other external forces trigger the 4D smart material’s response, leading to precise particle movement.
Applications & Potential Impact
IBM’s machine learning system also monitors these innovative materials for deviations or blockages, ensuring smooth operations with minimal human intervention.
Patent documents reveal that this design can deliver microparticles ranging from 1 to 100 microns in diameter. Its versatility across different media makes it ideal for various medical and industrial applications.
Medical & Tech Use Cases
- Targeted Drug Delivery: Physicians could use this technology to transport drugs through the bloodstream or gastrointestinal tract to specific cells.
- Microelectronics & Semiconductor Manufacturing: It could revolutionize the production of microelectronics and semiconductor components.
The Future of 4D Printing
4D printing builds upon 3D printing but takes it further—allowing printed materials to change shape dynamically when exposed to external stimuli. This innovation could lead to self-assembling structures and bio-inspired motion, similar to how single-celled organisms move through chemical reactions.
As IBM advances its 4D printing technology, this patented technology could redefine healthcare, nanotechnology, and industrial automation.