As the clock ticks into 2025, digital technologies will continue to reshape the manufacturing industry.
By Zvi Feuer, Senior Vice President, Digital Manufacturing Software Solutions, Siemens Digital Industries Software
As the clock ticks into 2025, digital technologies will continue to reshape the manufacturing industry. According to a Deloitte Research Center for Energy & Industrials report from 2019, 83 percent of manufacturers believe that digital solutions will revolutionize the way products are made within the next five years. Six years later, the potential benefits have included significant gains in resource efficiency, labor productivity and product quality, as well as cost reductions and advances in safety and sustainability.
Industries are already seeing an increase in the number of companies — from start-ups to small job shops and large OEMs — using digitalization to simulate and optimize their products and processes before they open a new factory. Then, once it is in operation, they can leverage the comprehensive manufacturing data that is collected on the factory floor to anticipate and refine production workflows. Furthermore, they can use this digital transformation to optimize production while increasing sustainability and ensuring their future in manufacturing. After 40 years in this business, I am excited to see how these transformations will redefine what is possible in manufacturing.
Digital threads are the pillars of digital transformation
Many companies in the world have adopted CAD tools for the digital transformation of product design and development. But few have adopted digital transformation capabilities for manufacturing, planning, production, optimization, logistics, supply chain and the managing of services and products in use. These are key areas of emphasis and something that companies need to work hard on. The digitalization of manufacturing and the planning of the production facility ensures that companies are more efficient, effective, resilient and agile.
By embracing a comprehensive digitalization strategy, manufacturers can digitally define entire workflows, enabling seamless collaboration between design, engineering and manufacturing. Products can be designed, simulated and produced in the digital world before doing so in the real world. This can enable a much higher utilization of production facilities, which means increased automation, the usage of more robotics and more smart operations and operators empowered by cloud computing and AI. As evidence, digital manufacturing is already being embraced by many industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics and healthcare.
Digital threads are the communication links between solutions and are built for various products. These products must be well-connected to “play well together.” Customers see the value in the end-to-end communication chain, but they do not necessarily need to deploy it throughout every process or equipment. It is important to provide flexibility so customers can customize the solution for their specific needs. For instance, a manufacturer can pick a single solution, such as CAD/CAM software, to start and then extend their solutions while creating an end-to-end digital thread. But they need to know that all these different components are going to work together in the digital thread, enabling the information to flow from product development to the shop floor and back.

For example, Siemens created a comprehensive digital twin of its motors and drives factory in Nanjing, China. This enabled extensive analysis in the digital world before making any real investment. By simulating various scenarios like the interactions between robots, AGVs and humans, engineers could optimize processes in the virtual environment. Thus, Siemens was able to reduce costs and ensure that the final facility operated smoothly from day one. This approach not only enhanced operational efficiency but also reduced risk and accelerated Siemens’ time-to-market, providing significant benefits to the company and its customers.
By integrating key digital technologies (such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, the industrial metaverse and big data analytics) into production processes, industrial companies of all sizes can realize efficiency increases, reducing costs and gaining faster production cycles through real-time monitoring and automated decision-making, improving their manufacturing capabilities.
The impact of cloud technology
Advances in cloud computing are providing the manufacturing industry with scalable, cost-effective solutions that enhance operational efficiency. By enabling seamless data sharing and integration across different departments and locations, the cloud facilitates better collaboration.
The benefits of cloud technology are significant for companies of all sizes. They are even greater for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) as it democratizes access to advanced manufacturing tools for the creation of digital twins and to enable the digital thread. The total cost of ownership for software is reduced by minimizing upfront expenditures and ongoing maintenance and upgrade costs. SMBs can use the cloud to leverage digital manufacturing tools without the need for significant IT infrastructure investments. This accessibility enables SMBs to implement digital transformation strategies that might previously have been out of reach — when compared to large enterprises.

Overall, cloud computing is an enabler. By adopting cloud-based solutions, manufacturers of all sizes can achieve greater flexibility and agility, enabling them to quickly adapt to market changes and evolving customer demands, while also positioning them for success in a rapidly evolving industry. Additionally, the cloud supports artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) applications, which can optimize manufacturing operations and improve product quality. Additionally, the implementation of high-performance computing can enable companies to do things at a much faster pace.
Harnessing industrial AI
Advances in AI enable manufacturers to analyze the vast amounts of data they are collecting from the shop floor. This provides valuable insights that can improve efficiency and reduce errors. Using copilots or AI to automate complex tasks frees up valuable resources and personnel. This can transform intricate documents into actionable processes that speed up operations and minimize mistakes. For instance, in the digital thread example above, AI is used for the generative design of 3D printed parts and for feature-based machining of complex components using automated CNC programming. This enables non-expert users to complete expert-level tasks without the need for advanced training or years of experience.
By leveraging AI, manufacturers can better utilize their digital twins to predict maintenance needs, reduce downtime and extend the lifespan of equipment. This can help manufacturers with both productivity and sustainability targets. It also can assist companies in making informed decisions about resource utilization, ensuring raw materials are used efficiently and cost-effectively.

Overall, AI has the potential to deliver significant benefits to manufacturers while helping to ease their digital transformation.
In addition, AI and cloud technology will play a critical role in the development and use of innovative technologies and manufacturing techniques, like the industrial metaverse.
Venturing into the industrial metaverse
The industrial metaverse represents an evolution in manufacturing that brings together all the digital technologies previously discussed to transform the future of manufacturing. It leverages the comprehensive digital twins of product and production, combined with information from edge devices and IoT sensors, to deliver a cohesive, physics-based digital environment that mirrors the real world and can be monitored and adjusted in real-time.
By providing enhanced visualization, collaboration and decision-making tools while leveraging advanced GPUs and AI, the industrial metaverse has the potential to revolutionize the industry. It enables companies to experience the digital world as if it were real, helping them to anticipate potential issues and optimize operations before any physical production begins, significantly reducing costs and improving efficiency.
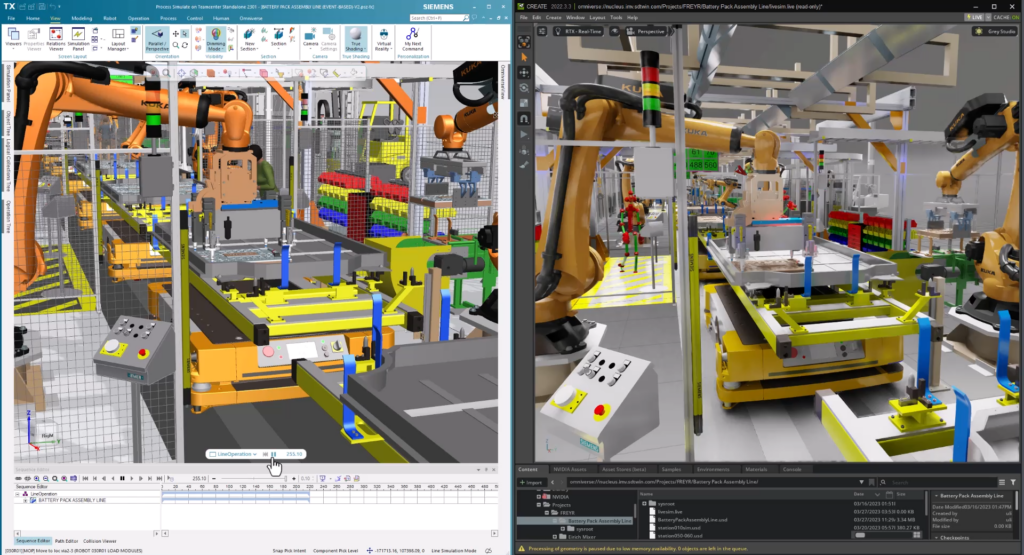
This immersive digital space will be enabled by the cloud, which provides the infrastructure companies need to store and process the massive amounts of data generated by the metaverse. The cloud also facilitates enhanced collaboration as it enables the sharing of data across departments and ecosystems.
Siemens is working with forward looking companies like FREYR, a Norwegian clean battery producer, to demonstrate how the industrial metaverse can help manufacturers collaborate and work in the future.
As more companies adopt this technology, the ability to leverage the digital thread and create detailed digital twins of manufacturing facilities will become standard practice. Customers will benefit from better collaboration and decision-making, faster time-to-market, improved product quality and more sustainable manufacturing practices.
The future of manufacturing
The digital transformation of manufacturing is not just a trend but a fundamental shift that is reshaping the industry. By embracing digitalization, manufacturers can bring together data, cloud computing, artificial intelligence and the industrial metaverse to reduce operational expenses, increase throughput and boost profits. This approach helps them achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency and productivity. This shift not only promises greater agility and resilience in manufacturing but also paves the way for competitive pricing and sustainable practices, ensuring a robust future for global industry.
Visit Siemens to learn more.
About the author:

Zvi Feuer is senior vice president of Digital Manufacturing Software Solutions for Siemens Digital Industries Software, a business unit of Siemens Digital Industries. Digital Manufacturing Software develops software products to deliver world-class solutions for manufacturing (part & assembly) planning, simulation, validation and operations (MES, scheduling, quality and automation).
In his current role, his responsibilities include leading global teams and initiatives to develop and service customers worldwide by providing Digital Manufacturing Software solutions that range from optimization of production and service facilities, design of assembly lines, development and validation of production systems, to the programming of CNC machines for managing production lines and plants.
Feuer has over 35 years of experience in enterprise software business management, with a primary focus in the manufacturing industries domain.